Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (15): 2345-2350.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.15.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Dynamic expression of Runx2 gene profile during osteogenesis in stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth
Wang Li-yuan 1, 2, Liu Da-yong1, Jia Zhi1
- 1 Dental Hospital, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China; 2 Tianjin Stomatological Hospital, Stomatological Hospital of Nankai University, Tianjin 300041, China
-
Online:2014-04-09Published:2014-04-09 -
Contact:Jia Zhi, Dental Hospital, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China -
About author:Wang Li-yuan, Master, Associate chief physician, Dental Hospital, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China; Tianjin Stomatological Hospital, Stomatological Hospital of Nankai University, Tianjin 300041, China -
Supported by:Scientific and Technology Development Project of Universities in Tianjin, No. 20110139
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Li-yuan, Liu Da-yong, Jia Zhi. Dynamic expression of Runx2 gene profile during osteogenesis in stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(15): 2345-2350.
share this article
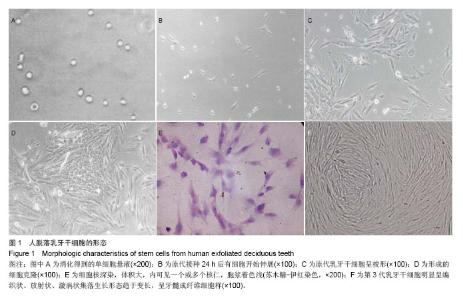
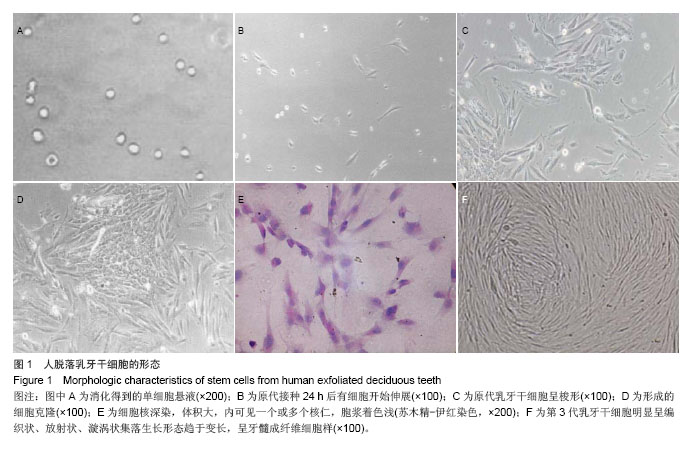
2.1 乳牙干细胞生长情况 人乳牙牙髓组织通过Ⅰ型胶原酶和dispase酶消化处理后,可获得单细胞悬液(图1A)。接种到培养瓶后,在倒置显微镜下观察,呈悬浮、折光性强的圆形细胞。细胞体积较小,胞浆均匀、明亮,边界光滑清晰。原代乳牙牙髓细胞接种约2 h后,即有细胞下沉固定不动,24 h后可见有细胞开始伸展(图1B),48 h基本展开。完全展开的细胞呈多形性,大部分呈梭形,成纤维细胞状,体积较小,轮廓清楚;少数为多角形、纺锤状或椭圆形(图1C)。之后,少数几个细胞迅速增殖,呈巢式或集落状生长,细胞间排列紧密,境界不清,周边细胞呈短梭形,体积较小(图1D),10-12 d细胞达到90%汇合。 苏木精-伊红染色观察可见胞核深染,卵圆形或圆形,胞核体积大,内可见一个或多个核仁,胞浆着色浅(图1E)。随着传代次数的增加,细胞的总数呈对数级上升。细胞明显呈编织状、放射状、漩涡状集落生长,形态趋于变长,呈牙髓成纤维细胞样(图1F)。"
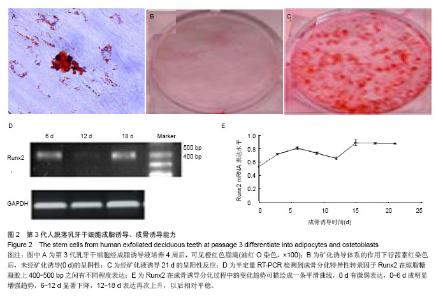
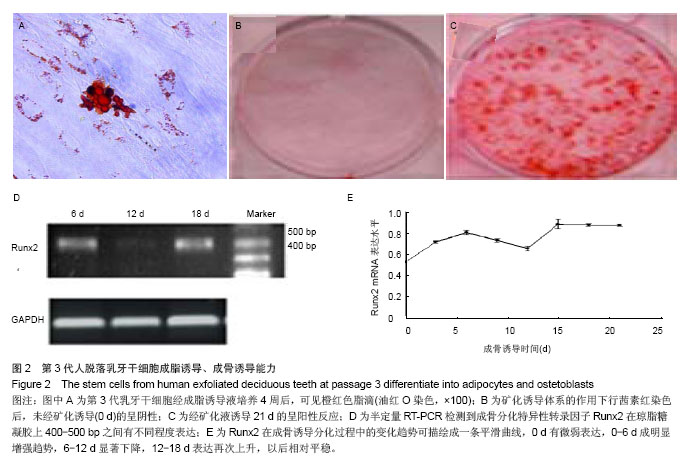
2.2 细胞表面抗原检测结果 STRO-1+占总细胞量的(20.01±1.62)%,CD146+占总细胞量的(92.51±1.34)%。 2.3 成脂诱导分化后油红O染色结果 成脂诱导体系培养4周,在相差显微镜下可见变大、变圆的胞体内有串珠样折光明显的脂滴。油红O染色可见橙红色阳性颗粒(图2A)。 2.4 成骨诱导细胞生长情况 诱导培养前2 d,在倒置显微镜下观察,细胞形态和数量没有明显变化。诱导培养4 d后,倒置显微镜下可观察到部分细胞体积增大,胞浆丰富,由原来的长梭形变为立方形,有些带有数个突起,呈星形、多角形。细胞排列呈一定的极性,少数有细长的突起。随着培养时间的延长,某些局部诱导后的细胞可重叠生长,呈结节状,随着细胞的不断增殖,最终铺满连成一片,可复层生长。 2.5 矿化结节形成能力 矿化诱导体系的作用下,前2 d生长缓慢,随后增殖加快,五六天单层长满皿底。八九天后,换液过程中发现较前阶段有较多的细胞漂浮死亡。10-12 d可观察到个别位置的细胞呈复层生长,透光性变差。15-17 d前后可见有散在的极细小沙粒样杂质贴敷培养皿底细胞表面,换液不能去除。行茜素红染色后,提示未经矿化诱导(0 d)的呈阴性(图2B),经矿化液诱导21 d的呈阳性反应(图2C),细胞内有钙盐沉积。 2.6 PCR检测结果 于成骨诱导不同时间点均可检测到成骨分化特异性转录因子Runx2在琼脂糖凝胶上400-500 bp之间有不同程度表达(图2D)。其在成骨诱导分化过程中的变化趋势可描绘成的一条平滑曲线(图2E)。0 d有微弱表达,0-6 d成明显增强趋势,6-12 d显著下降,12-18 d表达再次上升,以后相对平稳。"
| [1]Miura M, Gronthos S, Zhao M,et al. SHED: stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(10):5807-5812. [2]Laino G, Graziano A, d'Aquino R,et al. An approachable human adult stem cell source for hard-tissue engineering.J Cell Physiol. 2006;206(3):693-701. [3]Laino G, Carinci F, Graziano A, et al. In vitro bone production using stem cells derived from human dental pulp.J Craniofac Surg. 2006;17(3):511-515. [4]Laino G, d'Aquino R, Graziano A,et al.A new population of human adult dental pulp stem cells: a useful source of living autologous fibrous bone tissue (LAB).J Bone Miner Res. 2005; 20(8):1394-1402. [5]Gronthos S, Mankani M, Brahim J,et al.Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25):13625-13630. [6]Gimble JM, Morgan C, Kelly K, et al.Bone morphogenetic proteins inhibit adipocyte differentiation by bone marrow stromal cells.J Cell Biochem. 1995;58(3):393-402. [7]Graf T, Stadtfeld M.Heterogeneity of embryonic and adult stem cells.Cell Stem Cell. 2008;3(5):480-483. [8]Pereira Lda V.The importance of the use of stem cells for public health.Cien Saude Colet. 2008;13(1):7-14. [9]Cuenca-López MD, Zamora-Navas P, García-Herrera JM,et al.Adult stem cells applied to tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2008; 54(1):40-51. [10]Friedenstein AJ, Chailakhyan RK, Gerasimov UV.Bone marrow osteogenic stem cells: in vitro cultivation and transplantation in diffusion chambers.Cell Tissue Kinet. 1987; 20(3):263-272. [11]Gronthos S, Brahim J, Li W, et al. Stem cell properties of human dental pulp stem cells.J Dent Res. 2002;81(8): 531-535. [12]Kramer PR, Nares S, Kramer SF,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells acquire characteristics of cells in the periodontal ligament in vitro. J Dent Res. 2004;83(1):27-34. [13]Harada H, Kettunen P, Jung HS,et al.Localization of putative stem cells in dental epithelium and their association with Notch and FGF signaling.J Cell Biol. 1999;147(1):105-120. [14]Nataatmadja MI, Orams HJ, Reade PC.An estimation of ameloblast generation time and of the ameloblast proliferative compartment of guinea pig teeth.J Biol Buccale. 1990;18(1): 35-41. [15]Yen AH, Sharpe PT.Stem cells and tooth tissue engineering.Cell Tissue Res. 2008;331(1):359-372. [16]Kerkis I, Caplan AI.Stem cells in dental pulp of deciduous teeth.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2012;18(2):129-138. [17]林乐,李旭,杨茂伟,等. 地塞米松对骨髓间充质干细胞Runx2表达的影响[J]. 山东医药,2009,49(26):28-29. [18]Kanno T, Takahashi T, Tsujisawa T,et al. Mechanical stress-mediated Runx2 activation is dependent on Ras/ERK1/2 MAPK signaling in osteoblasts.J Cell Biochem. 2007;101(5): 1266-1277. [19]Zhu J, Shimizu E, Zhang X,et al. EGFR signaling suppresses osteoblast differentiation and inhibits expression of master osteoblastic transcription factors Runx2 and Osterix.J Cell Biochem. 2011;112(7):1749-1760. [20]关键,程宗生,王健平,等.成骨细胞中Runx2对机械离心力刺激的响应[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志,2010, 28(1):38-40. [21]Bueno EM, Glowacki J.Cell-free and cell-based approaches for bone regeneration.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009;5(12): 685-697. [22]Seo MS, Hwang KG, Kim H, et al. Analysis of gene expression during odontogenic differentiation of cultured human dental pulp cells.Restor Dent Endod. 2012;37(3): 142-148. [23]Schroeder TM, Jensen ED, Westendorf JJ.Runx2: a master organizer of gene transcription in developing and maturing osteoblasts.Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2005;75(3): 213-225. [24]Komori T.Regulation of skeletal development by the Runx family of transcription factors.J Cell Biochem. 2005;95(3): 445-453. [25]Schroeder TM1, Jensen ED, Westendorf JJ. Runx2: a master organizer of gene transcription in developing and maturing osteoblasts.Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2005;75(3): 213-225. [26]Lengner CJ, Drissi H, Choi JY,et al. Activation of the bone-related Runx2/Cbfa1 promoter in mesenchymal condensations and developing chondrocytes of the axial skeleton.Mech Dev. 2002;114(1-2):167-170. [27]Teplyuk NM, Haupt LM, Ling L,et al.The osteogenic transcription factor Runx2 regulates components of the fibroblast growth factor/proteoglycan signaling axis in osteoblasts.J Cell Biochem. 2009;107(1):144-154. [28]de Crombrugghe B, Lefebvre V, Nakashima K.Regulatory mechanisms in the pathways of cartilage and bone formation.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001;13(6):721-727. [29]Komori T. Runx2, a multifunctional transcription factor in skeletal development.J Cell Biochem. 2002;87(1):1-8. [30]Jensen ED, Nair AK, Westendorf JJ. Histone deacetylase co-repressor complex control of Runx2 and bone formation.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2007;17(3):187-196. [31]Phillips JE, Gersbach CA, Wojtowicz AM,et al. Glucocorticoid-induced osteogenesis is negatively regulated by Runx2/Cbfa1 serine phosphorylation.J Cell Sci. 2006; 119(Pt 3):581-591. [32]Westendorf JJ, Zaidi SK, Cascino JE,et al. Runx2 (Cbfa1, AML-3) interacts with histone deacetylase 6 and represses the p21(CIP1/WAF1) promoter.Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22(22): 7982-7992. [33]Jin YH, Jeon EJ, Li QL,et al.Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates p300-dependent RUNX3 acetylation, which inhibits ubiquitination-mediated degradation.J Biol Chem. 2004;279 (28): 29409-29417. [34]Park OJ, Kim HJ, Woo KM,et al.FGF2-activated ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase enhances Runx2 acetylation and stabilization.J Biol Chem. 2010;285(6):3568-3574. [35]Jensen ED, Gopalakrishnan R, Westendorf JJ. Regulation of gene expression in osteoblasts.Biofactors. 2010;36(1):25-32. [36]Purpura KA, Aubin JE, Zandstra PW.Sustained in vitro expansion of bone progenitors is cell density dependent.Stem Cells. 2004;22(1):39-50. [37]Kärner E, Bäckesjö CM, Cedervall J,et al.Dynamics of gene expression during bone matrix formation in osteogenic cultures derived from human embryonic stem cells in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1790(2):110-118. [38]Pregizer S, Baniwal SK, Yan X,et al.Progressive recruitment of Runx2 to genomic targets despite decreasing expression during osteoblast differentiation.J Cell Biochem. 2008;105(4): 965-970. [39]Jiang H, Sodek J, Karsenty G,et al.Expression of core binding factor Osf2/Cbfa-1 and bone sialoprotein in tooth development. Mech Dev. 1999;81(1-2):169-173. [40]Chen S, Gu TT, Sreenath T,et al.Spatial expression of Cbfa1/Runx2 isoforms in teeth and characterization of binding sites in the DSPP gene.Connect Tissue Res. 2002;43(2-3): 338-344. [41]文军,陆群,倪龙兴. Runx 2在第三期牙本质形成过程中的分布及其意义[J]. 牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2008,18(5):251-254. [42]Yoda S, Suda N, Kitahara Y,et al.Delayed tooth eruption and suppressed osteoclast number in the eruption pathway of heterozygous Runx2/Cbfa1 knockout mice.Arch Oral Biol. 2004;49(6):435-442. [43]李昊妍,梁景平,吴安平,等.Cbfa1/Runt2在牙髓组织和牙髓干细胞中的表达研究[J]. 临床口腔医学杂志,2005,21(8):466-467. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [14] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [15] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||